Guide to deploying SSL certificates for intranet website systems
April 7, 2025
Please indicate when reprinting: Reprinted from ZoTrus CEO Blog)
Intranet refers to an internal network that is not connected to the public network (Internet). Intranet website system refers to a Web system used for internal business management. To ensure the data security of the internal management system, the intranet website system must also deploy an SSL certificate. However, the commonly used SSL certificates do not support intranet IP addresses and internal domain names, because CA cannot validate the user's control over the intranet IP address and internal domain name bound to the SSL certificate. What should we do? This guide is to explain in detail how to deploy an SSL certificate for an intranet website system, especially how to deploy an intranet SSL certificate bound to an intranet IP address.
1. Intranet traffic needs SSL certificates to implement HTTPS encryption protection
The reason why the internal network is called an intranet is that its traffic is all confidential data and cannot be connected to the public network to protect the security of these internal confidential information. However, the intranet is no longer a network within a switch in an office, but an intranet that spans floors, buildings, and even cities. If internal confidential data is circulated in plain text HTTP mode, it is very unsecure and very easy to be illegally stolen and tampered with in the transmission. Therefore, it needs encryption protection more than the public network.
As for how to implement encryption protection for intranet data, the simplest solution is to deploy SSL certificates for internal Websites to implement HTTPS encryption, rather than using an HSM to encrypt the original data and still transmit it using the plain text HTTP protocol. This solution is more expensive and complex to implement, and is not convenient for data processing and AI applications. The reason why the technical solution of using SSL certificates to implement transmission encryption is the easiest to implement and the lowest cost solution is that the entire application ecosystem supports this solution, including browsers and Web servers, and only SSL certificates need to be deployed.
2. Three options for deploying SSL certificates for intranet website systems
How to deploy SSL certificates for intranet websites has always been a problem that has troubled intranet administrators. Currently, there are only three technical solutions:
(1) Issue the self-signed SSL certificate
Issuing a self-signed SSL certificate is very simple. You only need to use OpenSSL software and a single line of command to do it:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 365 -nodes
Then enter the intranet IP address or host name to complete the issuance of the self-signed SSL certificate, which can be deployed on the Web server for use. The biggest problem is that it requires every intranet user to click to trust this self-signed SSL certificate when visiting the website for the first time.
(2) Use enterprise CA to issue intranet SSL certificate
If the enterprise CA has been established in the enterprise intranet, and the client certificates for intranet users to log in to the intranet system are issued, you only need to configure the SSL certificate issuance parameters to issue the intranet SSL certificate and deploy it for use. The intranet user computers have been set to trust the root certificate of the enterprise CA, if the key length of the issued intranet SSL certificate is RSA 2048 and SHA256 or above, common browsers should be able to implement HTTPS encryption normally.
(3) Apply for and deploy a publicly trusted SSL certificate
The only problem with the above two implementation methods is that common browsers do not trust self-signed certificates and SSL certificates issued by enterprise CA. It is necessary to install the root certificate and trust the self-signed certificate on each user's computer, which is also a relatively large workload. Therefore, users can also choose the third option, which is to apply for a publicly trusted SSL certificate.
This requires that the intranet has a DNS system, and that a publicly trusted SSL certificate is applied for using a public domain name. The public domain name is then resolved to the intranet IP address, and HTTPS encryption can be implemented using the SSL certificate bound to the public domain name. In this way, common browsers will not have unsafe warnings, and there is no need to install the enterprise CA root certificate or trust the self-signed certificate on each intranet user's computer.
3. Only by deploying an intranet SSL certificate that is trusted by browser can the security of intranet traffic be truly guaranteed.
From the three solutions provided above, it can be seen that browser trust is very important. The reason why the browser trusts it is because this SSL certificate is issued in accordance with international standards, which can ensure the security of keys and HTTPS encryption. Self-signed SSL certificates and certificates issued by enterprise CA are often impossible to fully comply with the international standard. This is the value of SSL certificates trusted by browsers.
Solution (3) above deploys an Internet SSL certificate trusted by browsers on the intranet, although it solves the problem of browser trust, but it does not solve the user requirement that the SSL certificate must be bound to a private IP address. After all, many existing intranets Web systems are accessed based on the intranet IP address, especially the intranet across organizations. It is difficult to implement a cross-organization intranet DNS resolution to resolve the public domain name to the internal IP address, and it is impossible to change all systems based on the intranet IP address to the public domain name for access.
ZoTrus fully realizes that users need to meet the two application requirements of binding intranet IP addresses and browser trust at the same time. It has taken more than two years to build an intranet SSL certificate application ecosystem. One of the core products is the CerSign brand intranet SSL certificate, it is a default dual-algorithm (RSA/SM2) SSL certificate, which supports binding intranet IP addresses and host names, solving the validation problem of binding intranet SSL certificates to intranet IP addresses; the second core product is ZT Browser. ZT Browser included and trusted the RSA and SM2 algorithm root CA certificates for issuing CerSign intranet SSL certificate. It not only trusts the dual-algorithm CerSign Intranet SSL certificate, but also it supports certificate transparency. ZT Browser gives priority to the SM2 algorithm to implement HTTPS encryption to meet the user's cryptography compliance requirements. For users who have installed ZT Browser, they can also use other commonly used browsers to implement RSA algorithm HTTPS encryption. These browsers also trust the CerSign RSA algorithm intranet SSL certificate.
It is precisely because the CerSign Intranet SSL Certificate meets the two core application needs of users that it has been welcomed by users after it was launched. Many users have applied for and deployed it, making contributions to ensuring the security of intranet traffic.
4. Only by achieving automatic management of intranet SSL certificates can we quickly popularize and implement HTTPS encryption of intranet traffic.
Although the CerSign Intranet SSL Certificate meets the two application requirements of users to bind the intranet SSL certificate and browser trust, it still requires manual application for the certificate like the Internet SSL certificate, and manual installation of the intranet SSL certificate on the intranet Web server. This certificate installation will affect the normal provision of Web services by running Web servers. Therefore, the intranet SSL certificate, like the Internet SSL certificate, also needs to be managed automatically.
ZoTrus Technology has launched the Intranet Edition of HTTPS Automation Gateway, which is another product innovation after the global first launch of the Internet Edition of HTTPS Automation Gateway in 2023. Because the intranet cannot connect to the Internet, it cannot connect to the ZoTrus Cloud SSL Service System, and it cannot achieve client-to-cloud integrated SSL certificate automation management. The only feasible solution is to achieve "self-sufficiency" of SSL certificates by the Intranet Gateway. ZoTrus Intranet Gateway has a built-in mini-CA system, a certified HSM card, and a dual-algorithm SSL issuing root certificate, which is used to automatically issue dual-algorithm intranet SSL certificates trusted by ZT Browser.
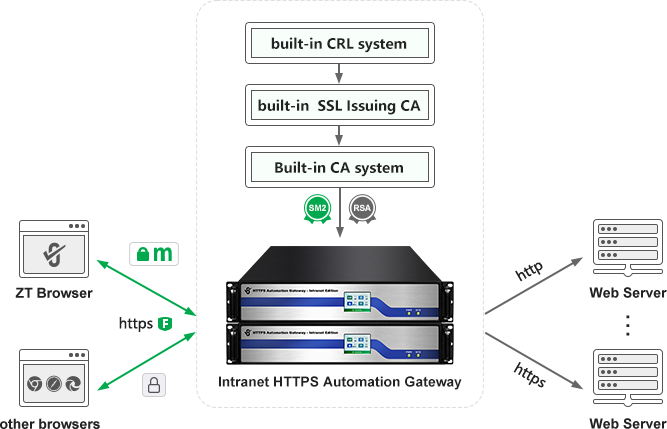
ZoTrus Intranet HTTPS Automation Gateway adopts the same technical approach as the Internet SSL Certificate Automation Management (ACME). It also solves the problem that the intranet cannot connect to the cloud SSL certificate automation management system, and achieves "self-sufficiency" of dual-algorithm intranet SSL certificates. It is more reliable than the Internet edition gateway that needs to rely on ACME cloud service, and completely solves the technical problem of naked plain text transmission of intranet traffic. It will definitely become the preferred product for solving the security of intranet traffic.
5. ZoTrus strives to create the best solution for deploying SSL certificates on intranet website systems
In addition to the three commonly used solutions on the market introduced in Section 2, users can choose the fourth solution created by ZoTrus Technology for the security of intranet traffic, which is:
(1) Deploying Intranet SSL Certificate:
Apply for an intranet SSL certificate online through the traditional manual method and manually install the intranet SSL certificate on the intranet Web server. It is recommended to purchase a 5-year validity certificate, which is guaranteed to be used for 5 years after one time installation, but this is only suitable for organizations with only a small number of internal Web servers.
(2) Deploying Intranet Gateway:
Deploy a ZoTrus Intranet HTTPS Automation Gateway, no need to apply and install the intranet SSL certificate, with zero modification of the original intranet Web server, and support up to 510 intranet Websites. The system automatically deploys a OV SSL certificate with a validity period of 90 days to achieve HTTPS encryption automation and WAF protection automation. The key and certificate are automatically updated every 80 days, and the HTTPS encryption automation is more secure and agile. This solution is suitable for organizations with a large number of intranet Web systems that run uninterruptedly, one time deployment for 5 years.
ZoTrus solution with two options can be used to ensure the security of intranet traffic (HTTPS encryption). ZT Browser is not only a browser, but also a PDF reader and encrypted email client, it trusts CerSign brand intranet SSL certificate and ZoTrus brand intranet SSL certificate autoconfigured by ZoTrus Intranet Gateway, it gives priority to using SM2 algorithm to implement HTTPS encryption, while other browsers implement RSA algorithm HTTPS encryption. It is recommended to deploy an Intranet HTTPS Automation Gateway in front of the intranet Web server to achieve a seamless upgrade from plaintext HTTP to HTTPS encryption without any modification. This truly ensures the security of intranet confidential data transmission, effectively ensures the security of intranet traffic, and meets user security and compliance requirements.