About the UI displaying the "Cybersecurity Protection Compliant (WAF)" icon
Whether a website is secure depends on at least four fundamental factors: HTTPS encryption, cryptography algorithm, WAF protection, and trusted identity validation. This is why ZT Browser's UI innovation displays four security-related icons:
. In addition to the security padlock, it also displays the cryptographic algorithm, WAF protection, and website trusted identity validation level. Please refer to the innovation UI Icon Summary of ZT Browser for details.
The browser, as the entrance to the Internet, user don’t know if the surfing website is secure. At present, various websites attacks have become the norm, and the website owner does not know whether its website has encountered attacks, unless it is an attack that the website obviously cannot access. Therefore, in order to enhance the security protection awareness of the website owners and website visitors, and meet the compliance requirements of the Cyber Security Law, ZT Browser exclusively displays the WAF protection icon in the address bar, so that the website visitors have seen the WAF protection of the website and cybersecurity protection compliant at a glance. This is also a technological innovation.

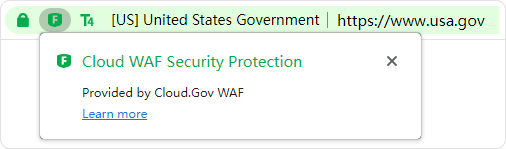
For websites that use the cloud WAF service that don’t pass the Cybersecurity Protection Compliant certification, it will display "Cloud WAF Security Protection".
For websites that have deployed ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway or ZoTrus WAF Automation Gateway, it displays as: Cybersecurity Protection Compliance, and it displays: Protected by ZoTrus Gateway WAF (******), where the ****** is the unique identifier of each ZoTrus Gateway deployed.
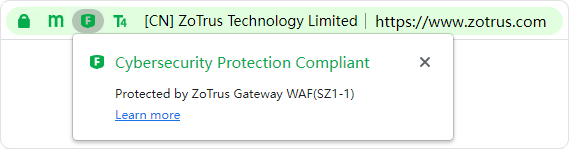
"Cybersecurity Protection" is the abbreviation of the Graded Protection of Cybersecurity. It is based on article 21 of "Cyber Security Law"–“The state shall implement the rules for graded protection of cybersecurity. Network operators shall, according to the requirements of the rules for graded protection of cybersecurity, fulfill the following security protection obligations, so as to ensure that the network is free from interference, damage or unauthorized access, and prevent online data from being leaked, stolen or tampered.” and article 31 – “The State implements focus protection for critical information infrastructure on the basis of the graded cybersecurity protection structure in important sectors and areas such as public telecommunications and information services, energy, transportation, irrigation works, finance, public services, e-government, etc., as well as other critical information infrastructure that, whenever it is destroyed, loses its ability to function or encounters data leaks, may gravely harm national security, the national economy, the people's livelihood and the public interest.” All websites must "adopt technical measures such as preventing computer viruses and cyber-attacks, network invasion and other hazardous cyber security behaviors" and "adopt technical measures such as data classification, important data backup and encryption" to ensure the website system security and meet the requirements of cybersecurity protection compliance.
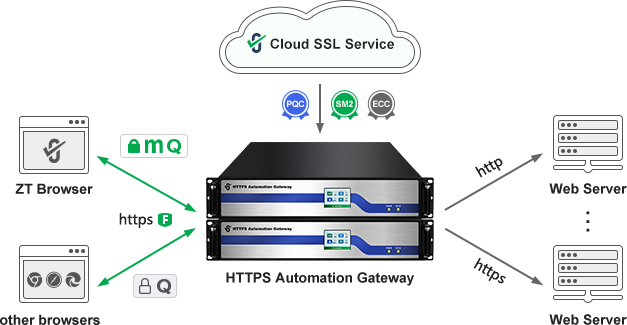
The first element of website security is HTTPS encryption, which encrypts information transmitted from the browser to the server, preventing confidential information from being leaked during transmission and effectively preventing illegal theft and tampering. This is a basic requirement. Without HTTPS encryption, all browsers will display the "Not secure" warning, which is a correct and accurate indication.
The second element is the cryptographic algorithm used for HTTPS encryption. If traditional cryptographic algorithms are used, data security is no longer guaranteed due to the "harvest now, decrypt later" security threat. Therefore, the second important icon of ZT Browser is the cryptographic algorithm used for HTTPS encryption. Learn more.
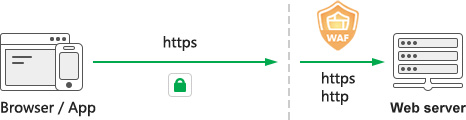
The third essential element is WAF protection, which is also indispensable. WAF can effectively prevent various attacks, preventing the illegal theft and tampering of information after it reaches the server from the browser. HTTPS encryption ensures the secure delivery of confidential information to the server, but once the information reaches the server, the task of preventing various attacks can only be performed by the Web Application Firewall (WAF). Without WAF protection, HTTPS encryption is meaningless! This is very important. HTTPS encryption and WAF protection each have their own responsibilities and areas of focus.
The fourth element is website trusted identity validation. A fake bank website may have HTTPS encryption, a security padlock icon displayed in the browser, and even WAF protection. However, these elements do not prove that the fake bank website is secure! Therefore, the website trusted identity validation is the fourth important element of website security, just as important as HTTPS encryption and WAF protection! The simplest website trusted identity validation is to deploy an IV SSL certificate, OV SSL certificate, or EV SSL certificate that has validated the website's identity. ZT Browser will correspond to display ,
,
icons. For websites that have only deployed DV SSL certificates that have not verified identity, ZT Browser will display
icon since the website identity is not validated. You can also apply for the Website Trusted Identity Validation Service of ZT Browser.
It is recommended to choose the ZoTrus HTTPS automation management solution, which does not need to apply for an SSL certificate from a CA, install an SSL certificate on the web server, or install ACME client software on the web server, and fully automatically implement https encryption and WAF protection. Since the validity period of SSL certificates will be shortened to 47 days, the traditional solution of manually applying for and deploying SSL certificates cannot meet the application requirements of many website systems that need to deploy SSL certificates, and the automatic management of SSL certificates must be realized. In particular, the critical information infrastructure system that needs to realize the SM2 algorithm HTTPS encryption, the solution that does not affect the normal operation of the existing business system with zero transformation of the original web server is required, ZoTrus solution not only automatically deploys the RSA/ECC SSL certificate, but also automatically deploys the SM2 SSL certificate to realize the automatic management of the dual-algorithm SSL certificate. ZT Browser preferentially uses the SM2 algorithm to achieve HTTPS encryption, and other browsers that do not support the SM2 algorithm use the ECC algorithm to achieve HTTPS encryption. For websites that already support the post-quantum hybrid cryptographic protocol, ZT Browser prioritizes the post-quantum hybrid cryptographic protocol for HTTPS encryption and displays "" icon the address bar.